Imagine a world where building a house is as easy as hitting “print.” That’s not just a dream anymore; it’s the reality of 3D printing. This revolutionary technology is turning the construction industry on its head, making homebuilding faster, cheaper, and a lot more fun. Forget about waiting months for your dream home—now you can watch it rise layer by layer, like a delicious cake that you can actually live in.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 3D Printing a House
3D printing technology revolutionizes the way houses are constructed. This method employs large-scale printers that use materials like concrete to create structures layer by layer. Unlike traditional methods, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, 3D printing reduces construction time significantly.
Cost savings emerge as another key benefit. Many studies show that 3D printing can cut construction costs by up to 40%. It lowers labor expenses since fewer workers are needed on-site. Environmentally friendly practices also play a role, as additive manufacturing minimizes waste compared to conventional building methods.
The process typically involves design software to create detailed models. Automated machines then follow these models, ensuring high precision. Architects and builders can collaboratively design homes with unique features tailored to individual preferences.
Significantly, 3D printing supports innovative architectural designs. It enables complex shapes and forms that traditional building methods might struggle to achieve. Customization options abound, allowing for unique aesthetics and energy-efficient configurations.
In addition, various projects around the world showcase the potential of this technology. Notable examples of 3D printed houses illustrate successful implementations in different climates and contexts. Many organizations continue to explore and refine the possibilities of 3D printing in residential construction.
Prominent companies are investing in the future of 3D printed homes. Developments in materials and technology promise even quicker builds and enhanced durability. Overall, 3D printing stands as a game changer, offering an efficient, sustainable approach to homebuilding.
Benefits of 3D Printing a House
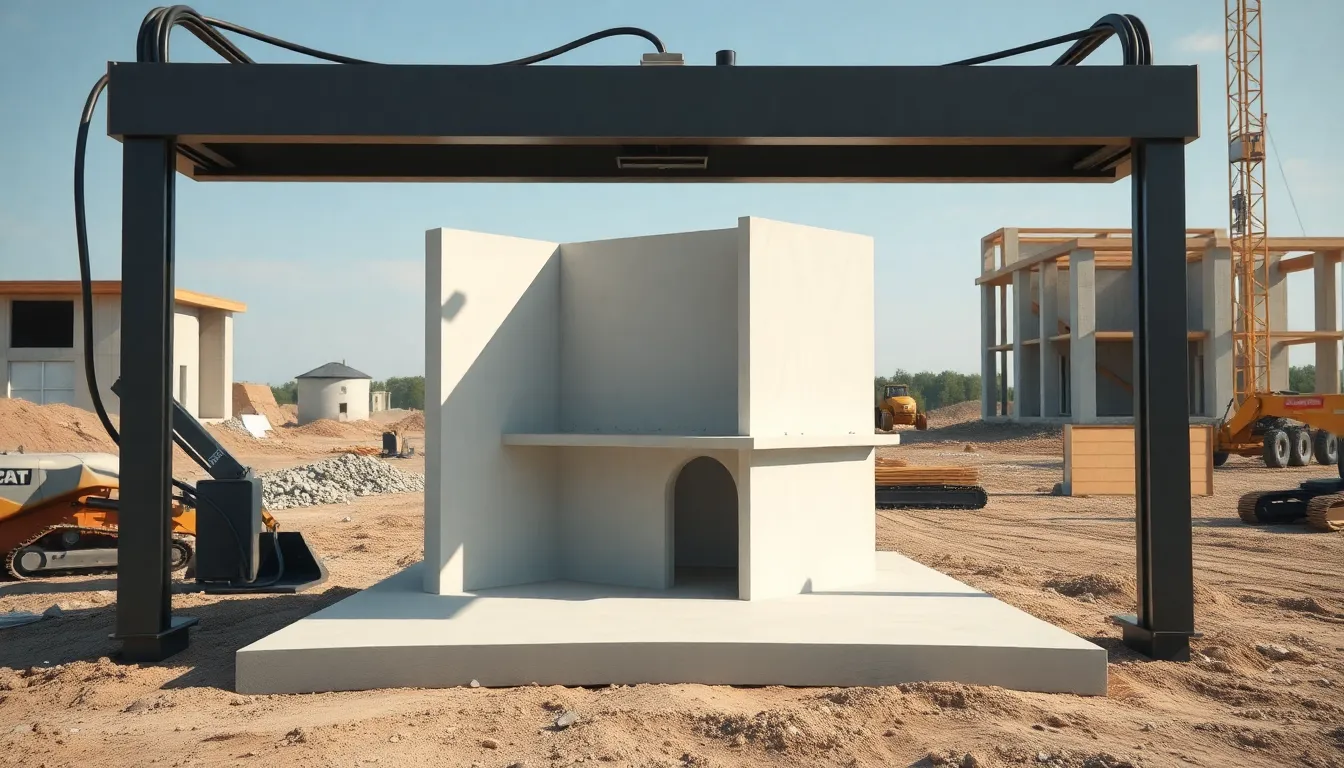
3D printing offers numerous advantages in home construction. This technology not only streamlines the building process but also brings significant savings.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency characterizes 3D printed homes. Construction costs can drop by up to 40% due to reduced labor expenses and material waste. Fewer workers are required on-site, as automated machines handle most tasks. Additionally, using concrete and other sustainable materials cuts down on expenditures associated with traditional building methods. The precise nature of 3D printing also minimizes errors, leading to less costly rework. This combination of factors positions 3D printing as a financial boon for homeowners and builders alike.
Speed of Construction
Speed of construction represents a key benefit of 3D printing. Homebuilding can occur in a matter of days instead of months. Large-scale printers lay down materials layer by layer, significantly accelerating the entire process. Architects and designers benefit from quick turnaround times, allowing them to iterate on designs rapidly. In urgent situations, such as disaster recovery or homelessness, this technology provides immediate solutions. The fast-paced nature of 3D printing meets the high demand for efficient housing, making it an attractive option for prospective homeowners.
The 3D Printing Process
The 3D printing process in home construction involves several key elements.
Materials Used
Concrete stands as the primary material for 3D printed homes. Various blends of concrete mix provide the necessary strength and durability. Researchers have also developed sustainable materials, including recycled plastics and composite materials, enhancing environmental benefits. These materials often require less energy to produce, aligning with eco-friendly initiatives. Certain projects utilize bio-based materials, which further reduce carbon footprints. Each material type contributes unique properties, allowing for diverse designs and finishes.
Technology Involved
Advanced technologies drive the 3D printing process. Large-scale printers employ robotic arms or gantry systems for precision layering. Specialized design software creates intricate digital models, streamlining the building process. CAD programs enable architects and engineers to customize designs before printing. Automatically, these machines translate digital blueprints into physical structures with accuracy. Integration of sensors and automation enhances the efficiency of construction, reducing human error. Continuous innovations in technology promise to improve speed, reduce production times, and lower costs even further.
Challenges in 3D Printing a House
3D printing a house presents several challenges that can hinder its widespread adoption. These challenges include regulatory issues and technical limitations that require careful consideration.
Regulatory Issues
Regulatory hurdles often complicate the implementation of 3D printing in construction. Building codes vary by location, and many jurisdictions lack updated regulations that accommodate this new technology. Compliance with existing codes can pose significant difficulties. Local governments may require extensive permitting processes, adding time and cost to projects. Safety standards must also be met, which can vary substantially. Different regions interpret regulations uniquely, creating inconsistencies across states and municipalities. Stakeholders need to engage with regulatory bodies to pave the way for smoother approvals.
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations frequently impact the effectiveness of 3D printing in home construction. The range of materials suitable for printing remains somewhat restricted, with concrete being the most common choice. Issues like material strength and durability also arise, affecting the quality of construction. The precision of the printing process can vary, particularly with intricate designs or large-scale models. Integration of various construction elements, such as plumbing and electrical systems, can complicate the building process. Continuous advancements in printer technology aim to address these limitations, yet further innovation is necessary for broader applications.
Future of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing technology continues to evolve in the construction sector, promising significant advancements in efficiency and sustainability. Ongoing developments in materials and techniques enhance the reliability and feasibility of 3D printed homes. Companies that invest in these innovations often focus on improving the speed of building while ensuring better durability for structures.
Innovations in design software play a crucial role as well. Enhanced modeling capabilities allow architects to create complex designs that were previously unachievable with traditional construction methods. Many construction firms leverage this technology to customize homes according to specific needs and preferences, increasing customer satisfaction.
Environmental considerations are also a priority. The adoption of materials like recycled plastics and bio-based substances contributes to reducing the carbon footprint associated with homebuilding. As the focus shifts toward sustainable practices, the construction industry can find ways to minimize waste and lower energy consumption during the building process.
Various successful projects worldwide demonstrate the versatility of 3D printing. Different climates and geographical locations have seen the benefits of this approach, proving its adaptability. Future initiatives will likely encourage more partnerships between governments and technology firms, facilitating faster regulatory processes to promote wider adoption.
Minimizing construction costs remains a priority for many homeowners. With potential savings of up to 40%, the affordability of 3D printed homes captures the attention of prospective buyers. Rapid construction timelines also prove advantageous in emergency situations, enabling quicker recovery after disasters or providing housing solutions for the homeless.
Current challenges include navigating regulatory issues. Many regions lack updated building codes to accommodate this technology, which can complicate approvals. Continuous advancements in the field are essential as technical limitations persist, yet the promise of innovative solutions keeps industry leaders optimistic about the future of 3D printing in construction.
The future of homebuilding is bright with 3D printing technology leading the charge. As it continues to evolve the construction industry is poised for a major transformation. The benefits of speed cost efficiency and sustainability make 3D printed homes an attractive option for many.
While challenges like regulatory hurdles and technical limitations remain ongoing advancements promise to address these issues. With increased investment and innovation the dream of affordable and customizable housing is becoming a reality. As this technology gains traction it could redefine how communities are built and how individuals experience homeownership.













