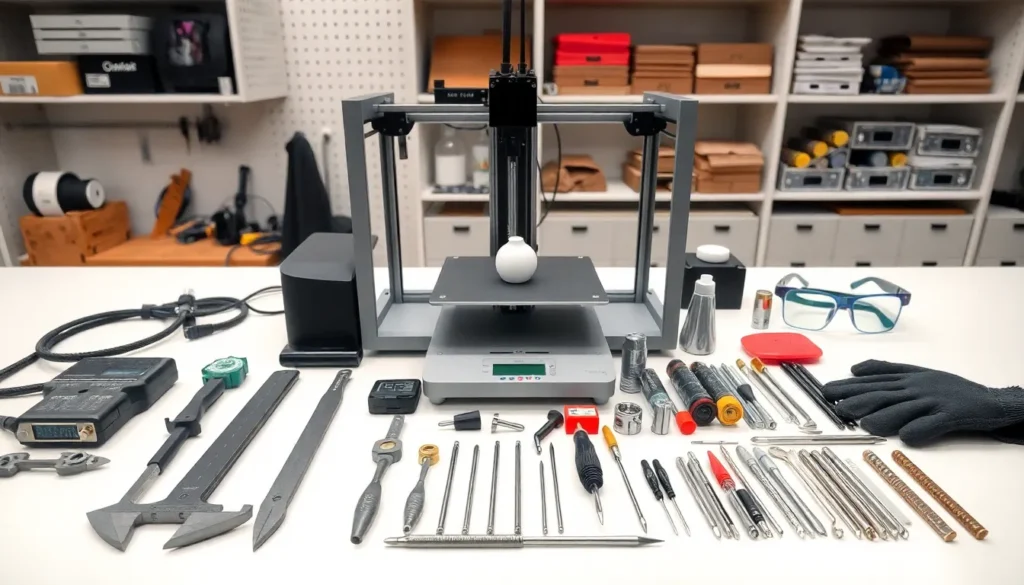
Every successful 3D print starts with the right 3D printing tools. A printer alone won’t get the job done. Makers need scrapers, files, calipers, and safety gear to produce quality results consistently. Whether someone is setting up their first machine or upgrading an existing workspace, the right toolkit makes a noticeable difference.
This guide covers the essential 3D printing tools that belong in every maker’s arsenal. From prep work to post-processing, maintenance to safety, each category plays a role in achieving cleaner prints and extending equipment life.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Takeaways
- Essential 3D printing tools include digital calipers, scrapers, flush cutters, and maintenance supplies to achieve consistent, high-quality prints.
- Pre-print preparation tools like bed leveling aids and adhesion sheets prevent common first-layer failures and reduce wasted filament.
- Post-processing tools such as needle files, sandpaper, and deburring blades transform rough prints into polished, professional-looking parts.
- Regular maintenance with brass brushes, cleaning needles, and lubricants extends your printer’s lifespan and prevents frustrating clogs.
- Safety gear—including ventilation systems, heat-resistant gloves, and respirators—protects makers from particles, fumes, and burns during printing and finishing.
- Keeping a spare parts kit with extra nozzles and PTFE tubes ensures quick repairs and minimizes downtime.
Pre-Print Preparation Tools
Good prints begin before the filament ever touches the build plate. Pre-print preparation tools help makers calibrate machines, prepare surfaces, and ensure models are ready to go.
Digital Calipers
Digital calipers are among the most important 3D printing tools for precision work. They measure filament diameter, check dimensional accuracy, and verify tolerances. A quality pair costs between $15 and $40 and pays for itself quickly. Makers use calipers to confirm their printer settings match real-world measurements.
Build Surface Adhesion Aids
First-layer adhesion determines print success. Many makers keep glue sticks, hairspray, or specialized adhesion sheets on hand. These 3D printing tools prevent warping and ensure parts stick properly during the build process. Blue painter’s tape remains a popular choice for PLA prints.
Spatulas and Scrapers
A good scraper removes finished prints without damaging the build plate. Flexible spatulas work well for most materials. Metal scrapers handle stubborn prints but require careful use to avoid scratches. Every maker should own at least two scrapers, one thin and flexible, one more rigid.
Bed Leveling Tools
Feeler gauges and leveling cards help achieve perfect first layers. These simple 3D printing tools cost only a few dollars but prevent hours of failed prints. Some makers prefer the paper method, while others invest in automatic bed leveling sensors.
Post-Processing and Finishing Tools
Raw prints rarely look perfect. Post-processing 3D printing tools transform rough models into polished finished products.
Flush Cutters and Nippers
Flush cutters remove support material cleanly. Quality nippers make precise cuts close to the model surface. Cheap cutters dull quickly and leave rough edges. Investing $10–$20 in good flush cutters saves time and frustration.
Needle Files and Sandpaper
Files smooth seams, remove layer lines, and refine details. A basic needle file set covers most finishing needs. Sandpaper in various grits, from 100 to 2000, enables progressive smoothing. Wet sanding with fine grits produces surprisingly smooth surfaces on many filament types.
Deburring Tools
Deburring tools clean up edges and holes quickly. They work especially well on functional prints that require precise fits. A simple deburring blade costs under $10 and handles most cleanup tasks.
Heat Guns and Lighters
Heat application removes stringing and softens edges. A small heat gun offers more control than an open flame. Some makers use lighters for quick touch-ups on small parts. These 3D printing tools require practice to avoid melting or deforming the model.
Maintenance and Cleaning Essentials
Printers require regular maintenance to perform well. The right cleaning tools extend machine life and prevent print failures.
Brass Brushes
Brass brushes clean nozzles without causing damage. They remove burnt filament and debris from the hotend. Regular brushing prevents clogs and maintains consistent extrusion. Makers should brush the nozzle before every few prints.
Nozzle Cleaning Needles
Accupuncture needles or specialized cleaning needles clear partial clogs. These thin 3D printing tools fit inside standard nozzle openings. Heating the nozzle first makes cleaning easier. A set of various sizes handles different nozzle diameters.
Isopropyl Alcohol and Cleaning Cloths
IPA (90% or higher concentration) removes oils and residue from build surfaces. Clean microfiber cloths prevent scratches. Wiping the bed before each print improves adhesion dramatically. This simple habit prevents many first-layer failures.
Lubricants
Linear rails and lead screws need periodic lubrication. White lithium grease works for most applications. PTFE-based lubricants suit high-temperature components. Proper lubrication reduces noise and extends mechanical component life.
Spare Parts Kit
Smart makers keep spare nozzles, PTFE tubes, and thermistors on hand. These 3D printing tools ensure quick repairs when components fail. A small parts organizer keeps everything accessible.
Safety Equipment for 3D Printing
Safety often gets overlooked in 3D printing setups. Proper safety 3D printing tools protect makers from real hazards.
Ventilation Systems
FDM printing releases ultrafine particles and VOCs (volatile organic compounds). An enclosure with filtration reduces exposure. Activated carbon filters absorb fumes effectively. At minimum, makers should print in well-ventilated spaces.
Respirators and Masks
N95 masks filter particles during sanding and post-processing. Respirators with organic vapor cartridges provide better protection when working with resin or certain filaments. ABS and resin require more protection than PLA.
Heat-Resistant Gloves
Hotends reach temperatures above 200°C. Heat-resistant gloves protect hands during nozzle changes and maintenance. Silicone-coated gloves offer grip and protection. Even brief contact with hot components causes serious burns.
Safety Glasses
Flying debris during cutting and sanding poses eye risks. Safety glasses cost under $10 and prevent injuries. Makers should wear them during any post-processing work.
Fire Safety
Smoke detectors and fire extinguishers belong near every printing station. Thermal runaway protection exists in modern firmware, but hardware failures still happen. A small ABC fire extinguisher provides peace of mind.